Spring Boot Export Data to Excel Example
Exporting data to Excel documents is a common feature of almost any applications. Through this article, I’m very glad to share with you guys my experience in implementing Excel export function in a Spring Boot application with the help of Apache POI Excel library.
Suppose that we have an existing Spring Boot project using Spring Data JPA and Hibernate to access data, Thymeleaf to render the view and MySQL as the database.The code examples below demonstrate how to retrieve information about users from the database, and generate an Excel file which the users can download onto their computers.1. Code of Entity Classes and Repositories Interfaces
We have the User entity class that maps to the users table in the database, as shown below:1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 | package com.vishesh;import javax.persistence.*;@Entity@Table(name = "roles")public class Role { @Id @GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY) private Integer id; private String name; private String description; // constructors, getter and setters are not shown for brevity } |
And code of the respective repository interfaces looks like this:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 | package com.vishesh;import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;public interface UserRepository extends JpaRepository<User, Integer> { }public interface RoleRepository extends CrudRepository<Role, Integer> { } |
These are simple, typical repositories as required by Spring Data JPA.
2. Declare Dependency for Excel Library
To generate Excel file, we need to use an external library and Apache POI is one of the most popular ones. So we need to declare the following dependency to use Apache POI for Excel in the Maven’s project file:1 2 3 4 5 | <dependency> <groupId>org.apache.poi</groupId> <artifactId>poi-ooxml</artifactId> <version>4.1.0</version></dependency> |
3. Code for the Service Class
In the service layer, we may have the UserServices class as follows:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 | package com.vishesh;import java.util.List;import javax.transaction.Transactional;import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;import org.springframework.data.domain.Sort;import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;@Service@Transactionalpublic class UserServices { @Autowired private UserRepository repo; public List<User> listAll() { return repo.findAll(Sort.by("email").ascending()); } } |
As you can see, the listAll() method delegates the call to the findAll() method of the UserRepository interface, which is implemented by Spring Data JPA (extended from JpaRepository). The listAll() method will be invoked to get data about users from the database.
4. Code Excel Exporter Class
Next, code a separate class that is responsible to generate an Excel document based on the input is a List collection of User objects, as shown below:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 | package com.vishesh;import java.io.IOException;import java.util.List;import javax.servlet.ServletOutputStream;import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Cell;import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.CellStyle;import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Row;import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFFont;import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFSheet;import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFWorkbook;public class UserExcelExporter { private XSSFWorkbook workbook; private XSSFSheet sheet; private List<User> listUsers; public UserExcelExporter(List<User> listUsers) { this.listUsers = listUsers; workbook = new XSSFWorkbook(); } private void writeHeaderLine() { sheet = workbook.createSheet("Users"); Row row = sheet.createRow(0); CellStyle style = workbook.createCellStyle(); XSSFFont font = workbook.createFont(); font.setBold(true); font.setFontHeight(16); style.setFont(font); createCell(row, 0, "User ID", style); createCell(row, 1, "E-mail", style); createCell(row, 2, "Full Name", style); createCell(row, 3, "Roles", style); createCell(row, 4, "Enabled", style); } private void createCell(Row row, int columnCount, Object value, CellStyle style) { sheet.autoSizeColumn(columnCount); Cell cell = row.createCell(columnCount); if (value instanceof Integer) { cell.setCellValue((Integer) value); } else if (value instanceof Boolean) { cell.setCellValue((Boolean) value); }else { cell.setCellValue((String) value); } cell.setCellStyle(style); } private void writeDataLines() { int rowCount = 1; CellStyle style = workbook.createCellStyle(); XSSFFont font = workbook.createFont(); font.setFontHeight(14); style.setFont(font); for (User user : listUsers) { Row row = sheet.createRow(rowCount++); int columnCount = 0; createCell(row, columnCount++, user.getId(), style); createCell(row, columnCount++, user.getEmail(), style); createCell(row, columnCount++, user.getFullName(), style); createCell(row, columnCount++, user.getRoles().toString(), style); createCell(row, columnCount++, user.isEnabled(), style); } } public void export(HttpServletResponse response) throws IOException { writeHeaderLine(); writeDataLines(); ServletOutputStream outputStream = response.getOutputStream(); workbook.write(outputStream); workbook.close(); outputStream.close(); }} |
5. Code Handler method in the Controller Class
Next, implement a handler method in a Spring MVC controller class – UserController – as follows:1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 | package com.vishesh;import java.io.IOException;import java.text.DateFormat;import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;import java.util.Date;import java.util.List;import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;@Controllerpublic class UserController { @Autowired private UserServices service; @GetMapping("/users/export/excel") public void exportToExcel(HttpServletResponse response) throws IOException { response.setContentType("application/octet-stream"); DateFormat dateFormatter = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd_HH:mm:ss"); String currentDateTime = dateFormatter.format(new Date()); String headerKey = "Content-Disposition"; String headerValue = "attachment; filename=users_" + currentDateTime + ".xlsx"; response.setHeader(headerKey, headerValue); List<User> listUsers = service.listAll(); UserExcelExporter excelExporter = new UserExcelExporter(listUsers); excelExporter.export(response); } } |
6. Add Export Excel Link in the View Page
We use HTML and Thymeleaf to create a hyperlink that allows the user to click to export data to Excel as follows:1 | <a th:href="/@{/users/export/excel}">Export to Excel</a> |
7. Test Export and Download Excel file
Click the hyperlink Export to Excel, the Spring Boot application will generate an Excel file and the browser will automatically download that file. The file name is something like this: users_2020-09-02_11-30-06.xlsx. Open this file using Microsoft Excel application, you would see the following screen: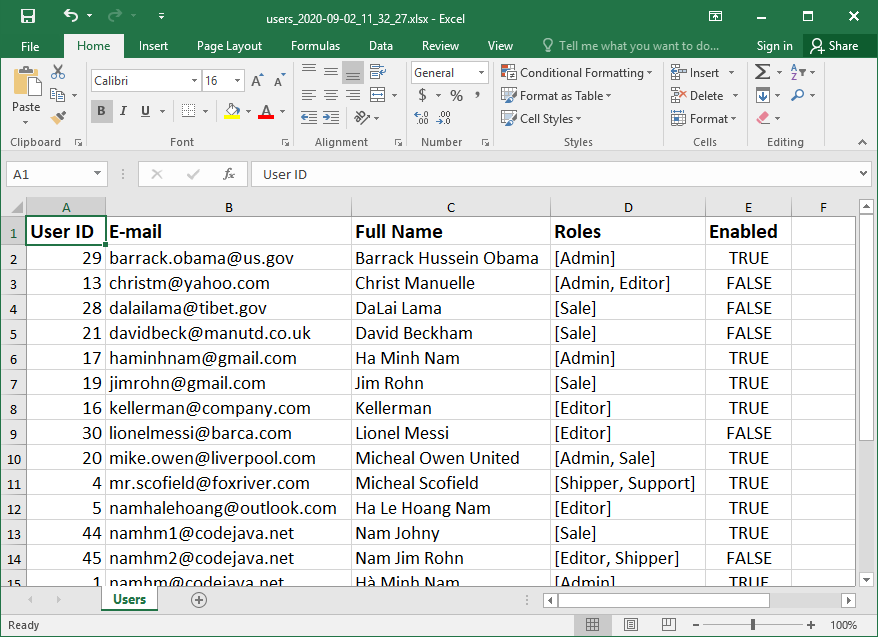
Conclusion
So far you have learned how to code Excel export function for a Spring Boot web application. You see, Spring Data JPA makes it easy to get data from the database, and Apache POI makes it easy to generate documents compatible with Microsoft Excel format.For video version of this tutorial, watch the video below:For Original Article, Please click on the link.

Helpful
ReplyDelete